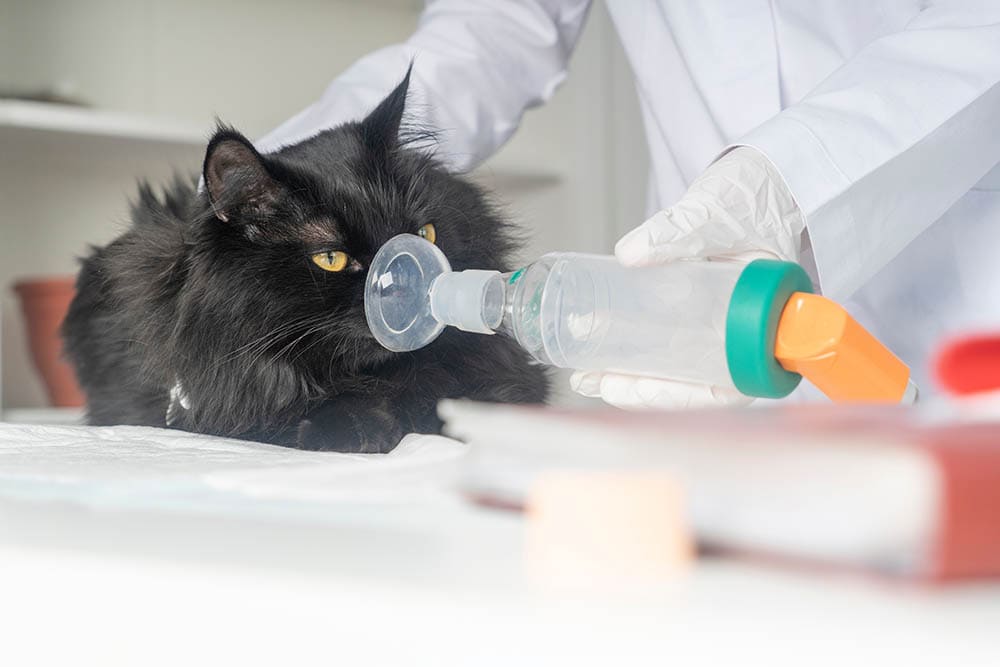
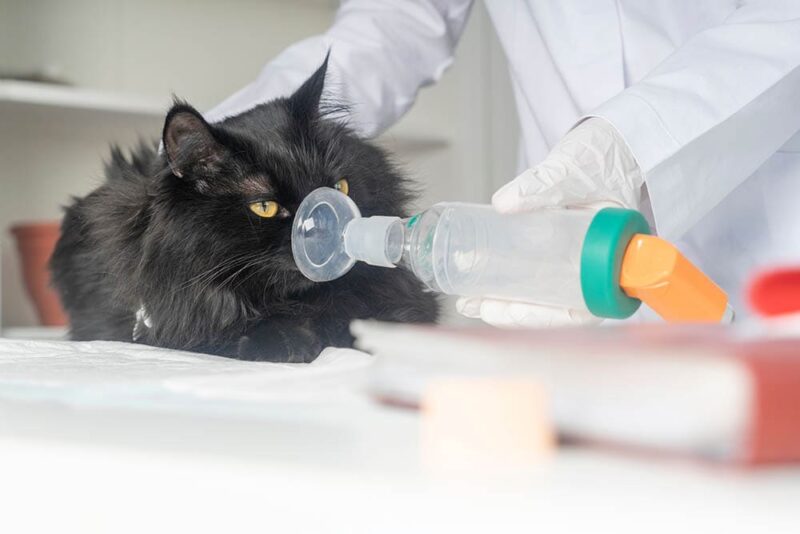
Fluid in the lungs, also known as pulmonary edema, is a serious condition that affects felines. If your cat receives this diagnosis from your veterinarian, you may wonder—what’s next? Why does my cat have fluid in their lungs, and what can be done to help them?
The following article will discuss pulmonary edema in cats, the symptoms and causes of this condition, and how it is diagnosed and treated. This will help you gain an understanding of what pulmonary edema may mean for your cat.

How Does a Cat’s Respiratory System Work?
The feline respiratory system functions to deliver oxygen to the lungs, where it is exchanged with carbon dioxide from the blood. In cats, the respiratory system is made up of large and small airways, and the lungs.
When a cat takes a breath, air travels down its trachea and into smaller tubes known as the left and right bronchi. From the bronchi, air moves into even smaller airways within the lungs that are called bronchioles. Bronchioles end in small sacs, known as alveoli, where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs.
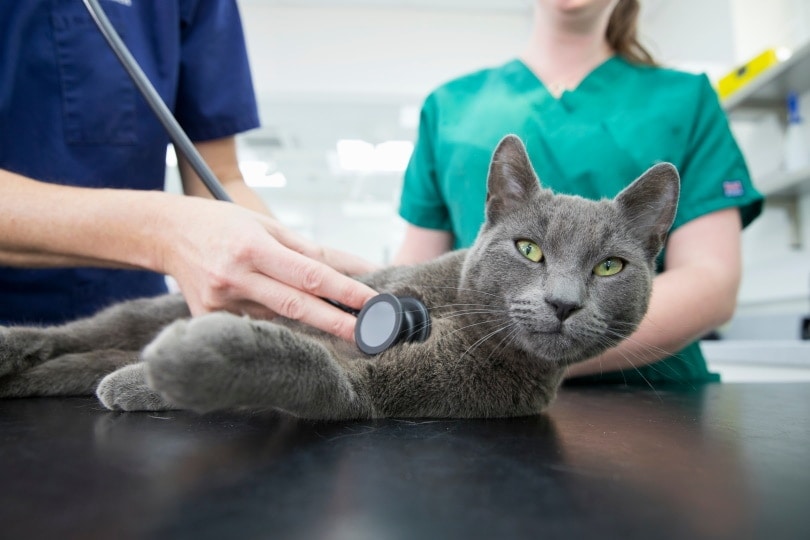
What is Pulmonary Edema?
Pulmonary edema is the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the alveoli of the lungs. When fluid builds up within the alveoli, gas exchange is negatively impacted, which results in poor oxygenation of the blood. A low blood oxygen level is problematic, as it will eventually lead to reduced functioning of organ systems and tissues within the body.
Pulmonary edema may be confused with pleural effusion, a condition in which fluid builds up in the space between the lungs and chest wall.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Edema
Symptoms of pulmonary edema in cats may vary, depending on the severity of fluid build-up, and the presence of any underlying conditions. However, cats with pulmonary edema often exhibit the following signs:
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid respiratory rate
- Open-mouthed breathing
- Coughing
- Cyanosis (having a blue or grey cast to the tongue, gums, or skin)
- Rapid heart rate
- Weakness or collapse
What Causes Pulmonary Edema in Cats?
Pulmonary edema is often referred to in terms of being either cardiogenic or non-cardiogenic.
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema occurs secondary to left-sided congestive heart failure (CHF). In felines, heart failure is most commonly caused by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
Common causes of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema in cats may include acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, and electrocution, among other conditions.
How is Pulmonary Edema Diagnosed?
Chest x-rays are the preferred test for diagnosing pulmonary edema. Your veterinarian will also perform a physical exam, and may note abnormal lung sounds, such as crackles or wheezes, a heart murmur, or an irregular heart rhythm while listening with their stethoscope.
Other diagnostic tests that may aid in a more specific diagnosis of cardiogenic pulmonary edema include an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart), and an NT-proBNP (a blood test used to evaluate for heart disease).
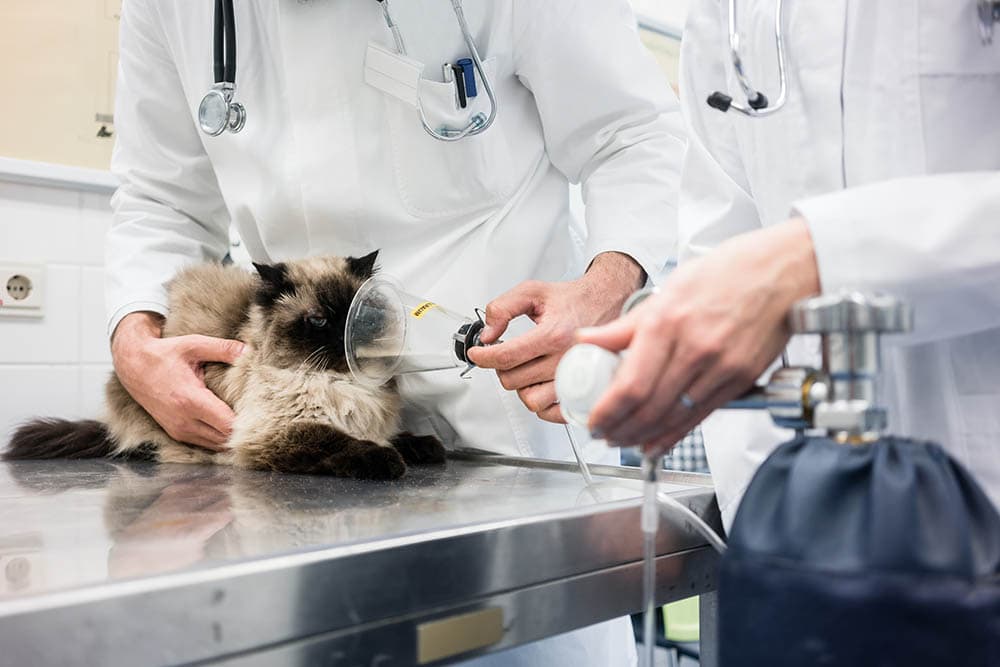
Treatment for Pulmonary Edema in Cats
Treatment for felines with pulmonary edema will depend on the underlying cause. Initial treatment for cases of cardiogenic pulmonary edema in cats will likely involve the following:
- Oxygen: Oxygen therapy is used to increase the level of oxygen in a cat’s blood. Cats will often be placed in an oxygen cage for this purpose.
- Diuretic medication: Furosemide (Lasix) is the most commonly used diuretic medication to treat cardiogenic pulmonary edema. However, other medications may be considered as well. Furosemide works at the level of the kidneys, and leads to the increased excretion of fluid via the urine.
- Rest: Rest and stress reduction are important for cats that may be struggling to breathe due to pulmonary edema. Pain-relievers or anti-anxiety medications may be used to help affected felines remain calm.
Oftentimes, treatment for cats with non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema is less clear-cut, but will typically also involve rest and oxygen therapy. Depending on the underlying cause, other medications such as antibiotics may be beneficial. Cats with severe cases of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema may need to be placed on a mechanical ventilator to help the lungs rest and recover.

What is the Prognosis for Pulmonary Edema?
Without prompt evaluation and treatment, pulmonary edema in cats will rapidly lead to respiratory distress and death. However, when treatment is initiated, the immediate prognosis for cases of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema in cats is fair.
Long-term prognosis is guarded, however, as heart disease such as HCM is typically progressive. With appropriate long-term medical management, the median survival times for cats with HCM and CHF are 92–563 days.
The prognosis for non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema varies depending on the underlying cause. Cases caused by electrocution may have a more favorable prognosis when compared to pulmonary edema secondary to ARDS, which carries a poor prognosis even with aggressive treatment.

Conclusion
In summary, pulmonary edema in cats is a serious condition requiring immediate veterinary attention. While treatment options and prognosis vary between cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, your veterinarian will be able to offer the most accurate information regarding what this condition may mean for the long-term health of your feline friend.
Featured Image Credit: Shveyn Irina, Shutterstock