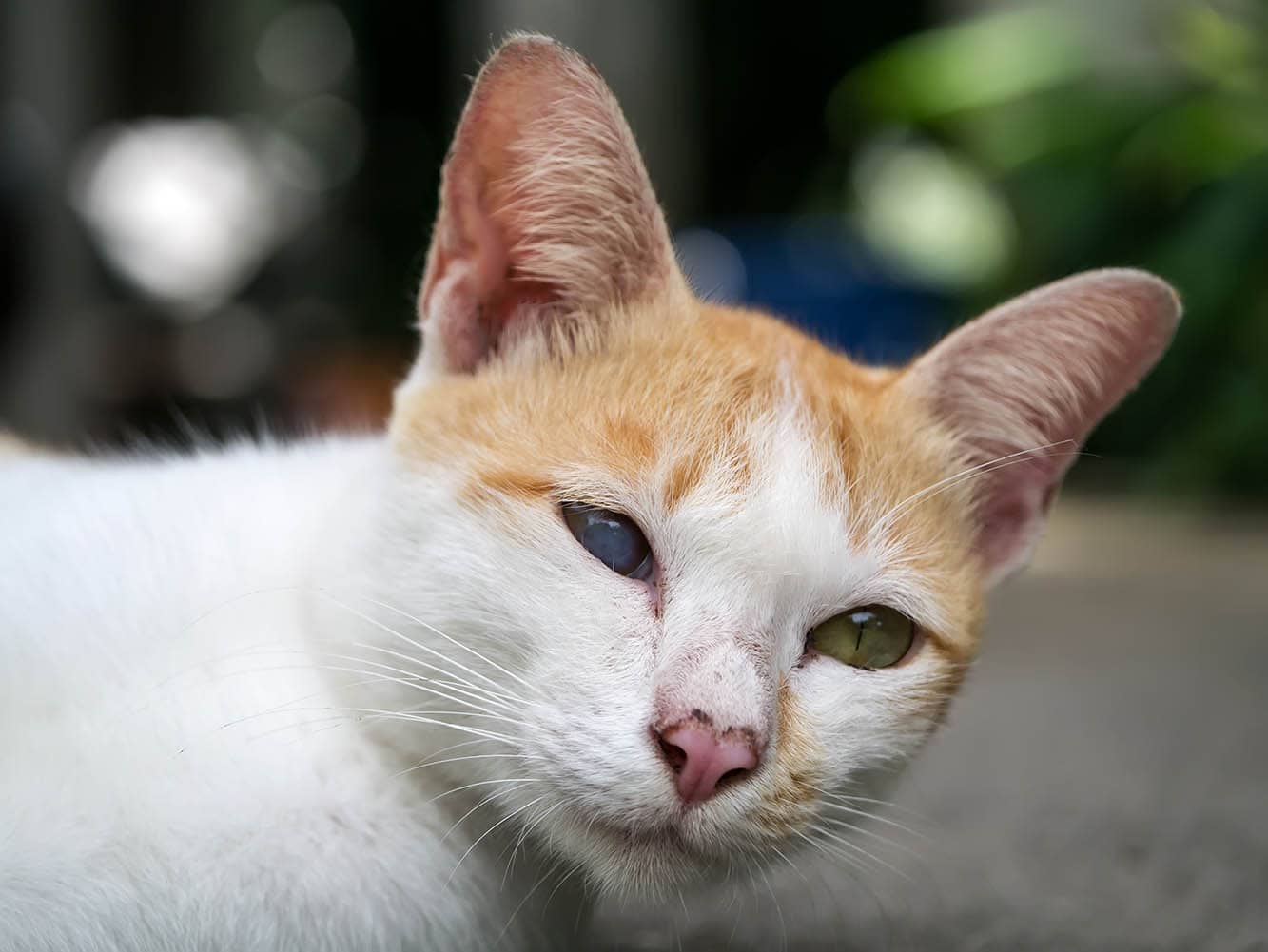
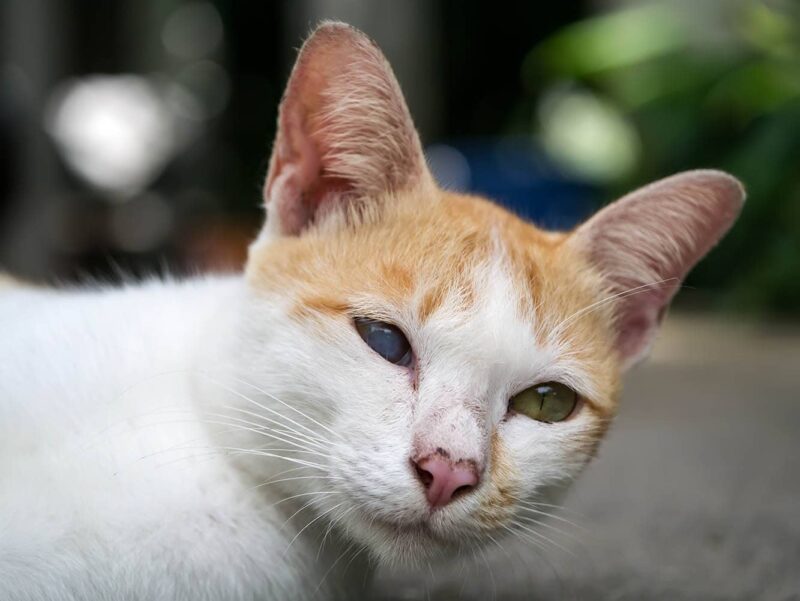
Iris atrophy refers to the condition that involves the degeneration of the iris, which is the colored part of the eye. The iris plays a crucial role in regulating the amount of light that enters the eye and and shapes the pupil.
Cats have acute senses that help them navigate and explore the world, including vision. In cats, iris atrophy is usually not a concerning condition that would affect their quality of life, and it rarely requires veterinary attention, but an accurate diagnosis must be made before assuming that the problem doesn’t need treatment. Here, we take a deeper look at iris atrophy among cats, what we can do, and when to see a veterinarian!
Click below to jump ahead:
- What Is the Iris in the Eye?
- What Is Iris Atrophy in Cats?
- Signs of Iris Atrophy in Cats
- Causes of Iris Atrophy in Cats
- When Should I Take My Cat to the Veterinarian?
- Treatment for a Cat With Iris Atrophy?
- FAQ

What Is the Iris in the Eye?
The iris is the part of the eye that gives it its color and is responsible for regulating the size of the pupil. It is composed of muscle fibers that control the dilation and constriction of the pupil in response to changes in light intensity.
The iris also helps to protect the delicate structures of the eye from harmful UV radiation and other environmental factors.
What Is Iris Atrophy in Cats?
Iris atrophy in cats refers to the thinning, weakening, or degeneration (atrophy) of the iris muscles, which can lead to a change in the shape, size, or color of the iris. Iris atrophy can affect different parts of the iris.
It doesn’t affect vision, but cats with iris atrophy can’t adapt as well to bright light and may develop sensitivity to bright light. The severity of iris atrophy can vary from mild to severe. It can also be unilateral, affecting one eye, or bilateral, affecting both eyes.
Iris atrophy is usually a natural part of the aging process and occurs mostly in older cats. In these circumstances, it is called senile iris atrophy. However, other eye issues can cause iris atrophy as well, such as uveitis (inflammation of the uvea, the internal tissue of the eye) and glaucoma. It is important to monitor your cat’s eyes regularly and consult with a veterinarian if you notice any changes in the appearance or behavior of your cat’s eyes.

What Are the Signs of Iris Atrophy in Cats?
The signs of iris atrophy in cats can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
Some common signs may include:
- Irregularly shaped pupils
- Uneven pupil sizes (anisocoria)
- Incomplete pupillary light reflex
- Increased sensitivity to light
- Mild changes in the iris color
It is important to note that these signs may also be indicative of other eye conditions, and a proper diagnosis can only be made by a qualified veterinarian through a comprehensive eye examination.
What Are the Causes of Iris Atrophy?
Iris atrophy in cats can have various causes, including age-related changes, inflammation, and underlying health conditions.
Age-related changes can contribute to iris atrophy in older cats, as the iris, like other parts of the body, can undergo degenerative changes with age.
Inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye, known as uveitis, can be another cause of iris atrophy in cats. Uveitis can be caused by various factors, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, or other underlying health conditions.
It is important to consult with a veterinarian for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis if you suspect your cat may be experiencing iris atrophy. Identifying the underlying cause of the condition is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment and management options for your cat’s specific needs.

When Should I Take My Cat to the Veterinarian?
If you notice any changes in your cat’s eyes, such as a change in iris color, irregularly shaped or sized pupils, increased sensitivity to light, or signs of inflammation or discomfort, it is essential to consult your veterinarian promptly. Your veterinarian can conduct a thorough eye examination, determine the underlying cause of the iris atrophy, and provide appropriate treatment or management options tailored to your cat’s specific needs.
How Do I Care for a Cat With Iris Atrophy?
Generally, iris atrophy is considered a benign process and requires no treatment unless there is another underlying condition. If so, the treatment will be aimed at the eye condition causing iris atrophy and may involve a combination of veterinary care and at-home management. Once your cat has been diagnosed with iris atrophy, your veterinarian will prescribe a treatment plan tailored to your cat’s specific needs. This may include medications to address underlying causes, such as antibiotics for infections, anti-inflammatory drugs for uveitis, or or drugs to lower the pressure inside the eye.
Regular follow-up consults with your veterinarian are crucial in monitoring the progression of the condition and making any necessary changes to the treatment plan. Your veterinarian may also provide recommendations on diet and lifestyle changes that may benefit your cat’s overall health and eye health.
In addition to prescribed medications, at-home care plays an important role in managing iris atrophy in cats. Proper eye health must be observed by keeping your cat’s eyes clean and lubricated with prescribed eye drops or ointments to prevent further irritation. To reduce the risk of infections, regular grooming is also necessary by keeping your cat’s face clean.
Changes in the house must also be observed by creating a safe environment for your cat. Keep your cat’s living space clean and free of hazards that could potentially harm their eyes, such as sharp objects or other animals that may scratch or bite. Observing your cat’s behavior and monitoring for any changes in their eyes, such as increased redness, discharge, or discomfort, is crucial.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can Iris Atrophy Be Cured?
Iris atrophy is generally considered a benign change, part of the aging process, and irreversible. If there is an underlying eye problem, its treatment may slow down the progression of the condition.
Is Iris Atrophy Painful or Uncomfortable for Cats?
Iris atrophy isn’t painful but it can cause light sensitivity. Some underlying eye conditions may cause discomfort or pain for cats, especially if there is associated inflammation or infection. Signs of discomfort include squinting, pawing at the eyes, or increased tearing. If you notice any signs of discomfort, it is crucial to seek veterinary attention promptly.

Can Iris Atrophy Lead to Blindness in Cats?
Iris atrophy does not affect vision per se, but it could increase sensitivity to light. It is also crucial to determine if there are any co-occurring eye pathologies that may cause blindness in your cat. Nonetheless, with appropriate management and treatment, the risk of vision loss can be minimized.

Conclusion
Iris atrophy in cats is usually a degenerative condition that affects the iris, which is the colored part of the eye. Aside from old age, it can, in rare cases, also be caused by trauma, inflammation, or glaucoma. If your cat shows any signs of iris atrophy, it is important to seek veterinary attention promptly for proper diagnosis and management.
Featured Image Credit: NOPPHARAT7824, Shutterstock






